The concept of a circular economy, which emphasizes minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency, is gaining momentum. Businesses are redesigning products for durability and recyclability, contributing to significant economic benefits while reducing environmental impact (IBM – United States).
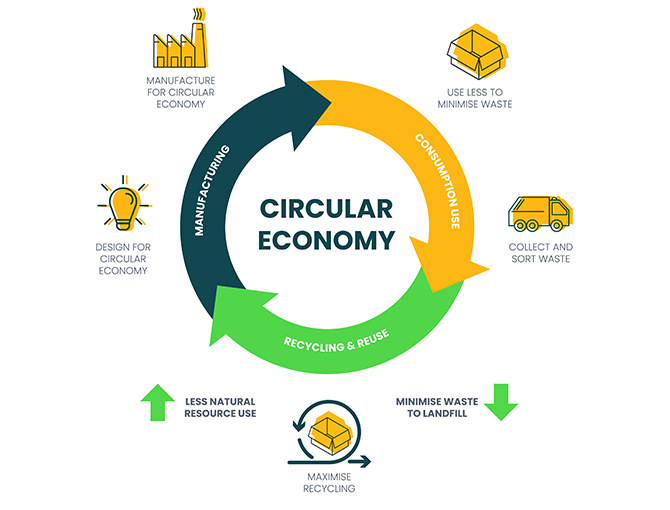
The concept of a circular economy focuses on designing waste out of production systems and maximizing the value of products and materials. It aims to create a closed-loop system where resources are continually reused, recycled, and regenerated, minimizing the need for new raw materials and reducing environmental impact. Here are key aspects and examples of circular economy practices:
Key Aspects of Circular Economy
- Design for Longevity: Products are designed to last longer, be easily repaired, and have modular components that can be updated or replaced. This reduces the frequency of disposal and the need for new products.
- Reuse and Repair: Encouraging the reuse of products and making repair services more accessible and affordable. This includes promoting second-hand markets, repair cafes, and manufacturer take-back schemes.
- Recycling and Upcycling: Materials from used products are recycled into new products, maintaining their value. Upcycling involves converting waste materials into new materials or products of better quality or for better environmental value.
- Product as a Service (PaaS): Businesses provide products as services rather than selling them. For example, customers can lease or rent items like clothing, electronics, or furniture, which the company maintains and refurbishes, extending their lifecycle.
- Sustainable Materials: Using renewable, biodegradable, or more easily recyclable materials in product design to ensure they can be fully reintegrated into the production cycle after use.
Examples of Circular Economy Practices
- Fashion Industry: Companies like Patagonia and H&M are adopting circular economy principles by offering recycling programs, repair services, and clothing rental options. Patagonia’s Worn Wear program encourages customers to buy second-hand items and repair old clothing (IBM – United States).
- Electronics: Fairphone designs smartphones that are modular and easy to repair. Customers can replace individual components like batteries and screens themselves, extending the device’s lifespan and reducing electronic waste (IBM – United States).
- Automotive Industry: Companies like Renault have established remanufacturing plants where used car parts are refurbished to like-new condition. This reduces the need for new raw materials and energy consumption (IBM – United States).
- Food and Agriculture: Circular practices in agriculture include composting organic waste to create natural fertilizers and using food waste to produce bioenergy. Companies like Loop are creating systems to return food packaging to manufacturers for reuse (IBM – United States) (Neste).
- Construction: The construction industry is adopting circular economy principles by using materials that can be easily dismantled and reused. Buildings are designed for deconstruction, and materials like steel and concrete are recycled into new construction projects (IBM – United States).
Benefits of Circular Economy
- Economic Gains: The circular economy is expected to generate significant economic benefits. For example, transitioning to a circular economy could generate up to $4.5 trillion in economic growth by 2030 (IBM – United States).
- Environmental Impact: By reducing waste and resource extraction, the circular economy helps mitigate climate change, decrease pollution, and preserve biodiversity.
- Resource Efficiency: Efficient use of resources reduces dependency on finite materials and enhances supply chain resilience.
Challenges and Considerations
- Regulatory Barriers: Different regulations and standards across regions can complicate the implementation of circular practices.
- Consumer Behavior: Changing consumer attitudes towards ownership and disposal is crucial for the success of circular models.
- Investment in Technology: Developing new technologies and systems for recycling, remanufacturing, and product tracking requires significant investment.
The circular economy represents a transformative approach to production and consumption that balances economic growth with environmental sustainability. It challenges traditional linear models and offers a pathway to a more sustainable future by keeping resources in use for as long as possible.