Our Take on Climate Change Action
When considering climate change action, it’s important to address a comprehensive range of factors to ensure effective and sustainable outcomes. Here are some key factors to consider:
Scientific Evidence and Data
- Climate Science
- Current State and Projections: It’s crucial to base climate policies and actions on the latest scientific research and climate models. This involves understanding current climate conditions, future projections, and the potential impacts of different levels of global warming.
- IPCC Reports: Regularly consulting the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports, which provide comprehensive assessments of climate science, can guide effective policy-making (Neste) (Nature).
- Monitoring and Reporting
- Emissions Tracking: Implement systems for accurately tracking greenhouse gas emissions at national, regional, and local levels. This includes setting up robust data collection mechanisms and reporting protocols.
- Impact Assessment: Regularly assess the environmental changes and the effectiveness of implemented climate strategies. Tools like remote sensing and satellite imagery can be invaluable for monitoring changes in land use, deforestation, and ice melt (Nature).
Policy and Governance
- International Agreements
- Paris Agreement: Align national actions with international commitments such as the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global temperature rise to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit the increase to 1.5°C (Neste).
- Global Cooperation: Engage in international cooperation to share technology, finance, and expertise. Participation in global forums and climate summits can facilitate collaborative efforts.
- National and Local Policies
- Renewable Energy Policies: Develop policies that promote the adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. This includes setting renewable energy targets and providing incentives for clean energy projects (Nature).
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Implement energy efficiency standards for buildings, vehicles, and appliances to reduce overall energy consumption and emissions (Neste).
- Regulatory Frameworks
- Environmental Regulations: Strengthen environmental regulations to reduce pollution and protect natural resources. This includes enforcing limits on industrial emissions and promoting sustainable land use practices.
- Compliance and Enforcement: Ensure robust mechanisms for monitoring compliance with climate regulations and enforcing penalties for non-compliance (Neste) (Nature).
Economic Considerations
- Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Economic Impact: Conduct comprehensive cost-benefit analyses to evaluate the economic impacts of climate actions, considering both the costs of implementation and the benefits of avoided climate damage.
- Long-term Planning: Develop long-term economic strategies that incorporate climate resilience and sustainability, ensuring economic growth does not come at the expense of the environment (Neste) (Nature).
- Green Financing
- Climate Finance: Secure funding for climate initiatives through various sources, including public investments, private sector involvement, and international financial support. Green bonds, climate funds, and development bank loans are essential tools.
- Incentives: Provide financial incentives for businesses and individuals to adopt sustainable practices. This can include tax breaks, subsidies for renewable energy, and grants for green projects (Nature).
- Market Mechanisms
- Carbon Pricing: Implement carbon pricing mechanisms such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems to internalize the environmental costs of greenhouse gas emissions and incentivize reductions (Neste).
- Subsidies and Support: Redirect subsidies from fossil fuels to renewable energy projects and energy-efficient technologies to promote a cleaner energy mix (Nature).
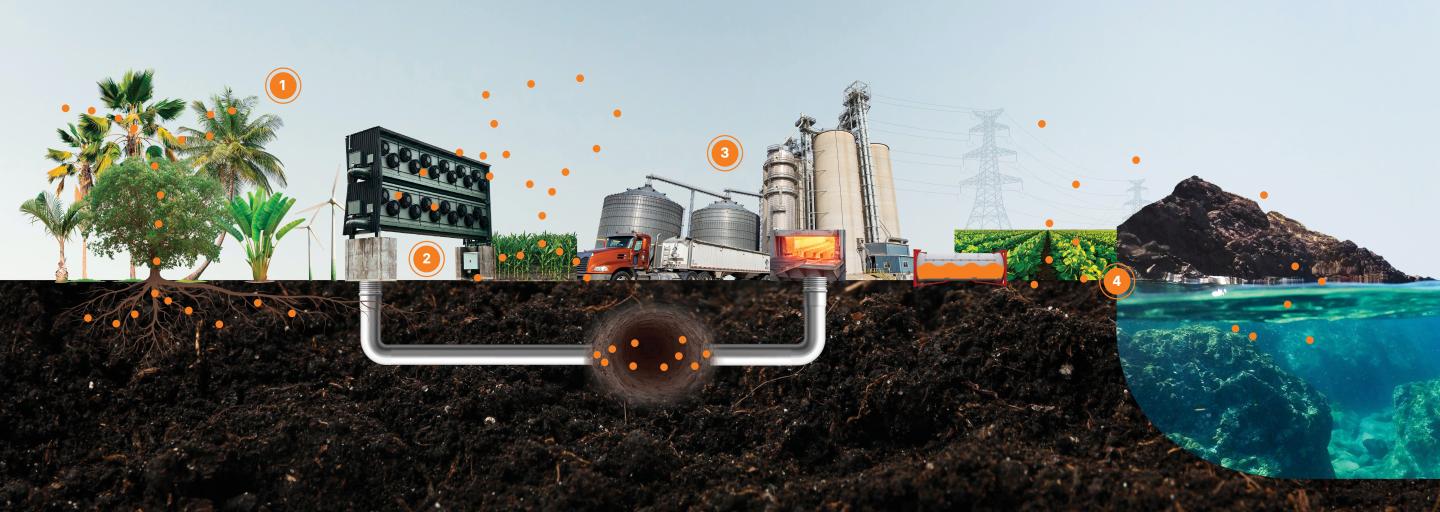
Technological Innovation
- Renewable Energy
- Deployment: Invest in the development and deployment of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower. This includes building infrastructure and supporting grid integration (Neste) (Nature).
- Storage Solutions: Develop and implement energy storage solutions to address the intermittency of renewable energy sources and ensure a stable energy supply.
- Energy Efficiency
- Technological Advancements: Promote the adoption of advanced technologies that improve energy efficiency across industries, buildings, and transportation sectors. This includes smart grids, energy-efficient appliances, and electric vehicles (Neste).
- Standards and Regulations: Implement strict energy efficiency standards and regulations to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Research and Development
- Innovation: Support research and development (R&D) in emerging technologies such as carbon capture and storage, advanced nuclear power, and sustainable materials. This can drive breakthroughs that significantly reduce emissions (Nature).
- Public-Private Partnerships: Encourage public-private partnerships to leverage resources and expertise for developing and commercializing new technologies (Nature).
Social and Cultural Dimensions
- Public Awareness and Education
- Climate Education: Raise awareness about climate change and its impacts through education programs, public campaigns, and media outreach. Educating the public on sustainable practices and the importance of climate action can build broader support for necessary policies (Neste).
- Behavioral Change: Promote behavioral change by encouraging sustainable lifestyles, such as reducing energy consumption, recycling, and using public transportation (Nature).
- Community Engagement
- Inclusive Participation: Involve local communities in decision-making processes and the implementation of climate policies. This can be achieved through public consultations, participatory budgeting, and engaging community groups (Nature).
- Local Solutions: Develop local solutions that address specific community needs and conditions, ensuring that climate actions are context-specific and effective (Neste).
- Equity and Justice
- Social Equity: Ensure that climate actions are inclusive and address the needs of vulnerable populations, promoting social equity and justice. This involves creating policies that protect low-income and marginalized communities from the adverse effects of climate change (Nature).
- Just Transition: Implement just transition strategies that support workers and communities transitioning from fossil fuel-dependent industries to sustainable employment opportunities (Nature).
Environmental Impact
- Biodiversity Protection
- Conservation: Integrate biodiversity conservation into climate strategies to protect ecosystems and species from the impacts of climate change. This includes establishing protected areas and restoring degraded habitats (Nature).
- Sustainable Practices: Promote sustainable practices in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem services (Neste).
- Land Use and Agriculture
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: Implement climate-smart agricultural practices that increase resilience, reduce emissions, and enhance carbon sequestration. Techniques include agroforestry, conservation tillage, and integrated pest management (Neste).
- Land Management: Develop sustainable land management policies that balance development needs with environmental protection, preventing deforestation and promoting reforestation (Nature).
- Water Resources
- Water Management: Manage water resources sustainably to adapt to changing precipitation patterns and ensure availability during climate extremes. This includes improving water use efficiency and protecting watersheds (Neste).
- Flood and Drought Management: Implement measures to mitigate the impacts of floods and droughts, such as building resilient infrastructure and adopting water-saving technologies (Nature).
Adaptation and Resilience
- Climate Resilience
- Resilient Infrastructure: Develop infrastructure that can withstand and adapt to the impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events. This includes building flood defenses, retrofitting buildings, and upgrading transportation networks (Neste) (Nature).
- Ecosystem-Based Adaptation: Utilize ecosystem-based adaptation approaches that enhance natural resilience, such as restoring wetlands and mangroves to protect against storm surges and coastal erosion (Nature).
- Disaster Risk Reduction
- Early Warning Systems: Implement early warning systems and emergency response plans to reduce the risks and impacts of climate-related disasters (Neste).
- Community Preparedness: Enhance community preparedness and response capabilities through training programs and public awareness campaigns (Nature).
- Health and Safety
- Public Health: Address the health impacts of climate change by strengthening healthcare systems, promoting public health measures, and ensuring access to clean water and sanitation (Nature).
- Heat and Pollution: Implement measures to protect against heatwaves and air pollution, such as creating green spaces in urban areas and monitoring air quality (Neste).